 Antidepressant drugs are the main treatment for mood disorders including anxiety and depression. Different antidepressant have different mechanisms of action, and these are not always fully understood. However, current theory suggests that for an antidepressant to be effective, it must normalise brain levels of monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, adrenaline and noradrenaline. This relates to the theory that lowered levels of these monoamines are a causative factor in the development of mood disorders, particularly depression. However, while low levels of monoamines are associated with mood disorders, it is unclear if the low levels are the cause or a consequence of the low mood. Interestingly, many of the antidepressant drugs also function as antioxidants in the brain. This has lead to speculation that antidepressant medication may be effective because it is able to lower levels of free radicals in the brain and in doing so protect the brain tissue from free radical induced lipid peroxidation.
Antidepressant drugs are the main treatment for mood disorders including anxiety and depression. Different antidepressant have different mechanisms of action, and these are not always fully understood. However, current theory suggests that for an antidepressant to be effective, it must normalise brain levels of monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, adrenaline and noradrenaline. This relates to the theory that lowered levels of these monoamines are a causative factor in the development of mood disorders, particularly depression. However, while low levels of monoamines are associated with mood disorders, it is unclear if the low levels are the cause or a consequence of the low mood. Interestingly, many of the antidepressant drugs also function as antioxidants in the brain. This has lead to speculation that antidepressant medication may be effective because it is able to lower levels of free radicals in the brain and in doing so protect the brain tissue from free radical induced lipid peroxidation.
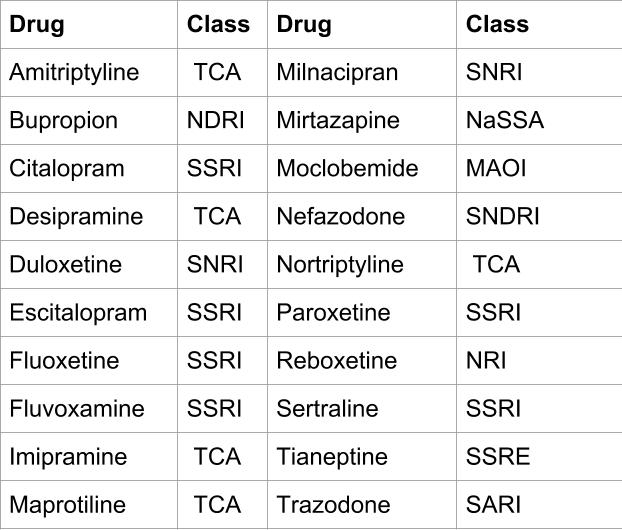
Antidepressant drugs that have been evidenced to have antioxidant effects. MAOI: monoamine oxidase inhibitor; NaSSA: noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant; NDRI: norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor; NRI: norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; SARI: serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor; SNDRI: serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor; SNRI: serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; SSRE: selective serotonin reuptake enhancer; SSRI: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TCA: tricyclic or tetracyclic antidepressant (Adapted from Behr et al., 2012).
For example, one group of researchers investigated the association between lipid peroxidation in the blood and mood. The results of the study showed that those with elevated levels of lipid peroxidation were at greatest risk of depression, particularly melancholic depression. Further, after treatment with selective reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant drugs for 3 months, the levels of lipid peroxidation in the blood decreased to normal levels. In addition, elevated levels of lipid peroxidation were accompanied by increased activity of antioxidant enzymes glutathione peroxidase, catalase and superoxide dismutase in depressed individual, suggesting a higher requirement for antioxidants in response to a higher level of free radicals. After treatment with SSRI drugs the levels of antioxidant enzymes returned to normal. Therefore free radical generation may be elevated in patients with depression, and the administration of SSRI drugs may provide antioxidant effects that explain their mood elevating effects.
Eat Well, Stay Healthy, Protect Yourself
RdB
