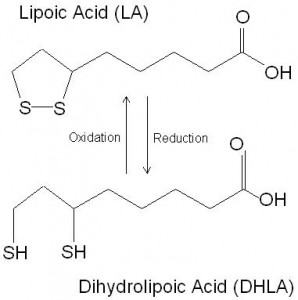
Alpha lipoic acid (thioctic acid) consists of carbon chain with two attached sulphur atoms, one on the sixth and one on the eighth carbon (figure 1). Reduction of lipoic acid causes the formation of dihydrolipoic acid and the formation of two thiol (SH) groups. Alpha lipoic acid can be synthesised in humans and is therefore not an essential nutrient, although dietary intake can increase tissue concentrations. Alpha lipoic acid plays two important roles in human metabolism, with both roles related to the presence of its sulphur atoms. Firstly, alpha lipoic acid can act as a cofactor to a number of enzymes involved in energy production including pyruvate dehydrogenase and 2-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Its second role is that of an antioxidant. Both roles are possible because its sulphur moieties are able to participate in the transfer of hydrogen atoms. Alpha lipoic acid is unusual amongst antioxidants, because it is able to act in both plasma membrane and cytosol of the cell environment, making it both a water soluble and lipid soluble antioxidant.
Alpha lipoic acid (thioctic acid) consists of carbon chain with two attached sulphur atoms, one on the sixth and one on the eighth carbon (figure 1). Reduction of lipoic acid causes the formation of dihydrolipoic acid and the formation of two thiol (SH) groups. Alpha lipoic acid can be synthesised in humans and is therefore not an essential nutrient, although dietary intake can increase tissue concentrations. Alpha lipoic acid plays two important roles in human metabolism, with both roles related to the presence of its sulphur atoms. Firstly, alpha lipoic acid can act as a cofactor to a number of enzymes involved in energy production including pyruvate dehydrogenase and 2-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Its second role is that of an antioxidant. Both roles are possible because its sulphur moieties are able to participate in the transfer of hydrogen atoms. Alpha lipoic acid is unusual amongst antioxidants, because it is able to act in both plasma membrane and cytosol of the cell environment, making it both a water soluble and lipid soluble antioxidant.
Figure 1. The structure of alpha lipoic acid and dihydrolipoic acid. The presence of the sulphur atoms are pivotal in its biological function.
Alpha lipoic acid has been used in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy, which likely relates to its in vivo antioxidant effects1. In this respect, alpha lipoic acid may be able to chelate metal ions, scavenge reactive oxygen species, regenerate endogenous antioxidants and repair oxidative damage. In animal experiments, the ability of alpha lipoic acid to prevent nerve damage, increase nerve regeneration and improve blood flow provides the rationale for its therapeutic use in diabetes. In addition, alpha lipoic acid may have a direct effect on blood sugar control, possibly through an ability to increase insulin sensitivity. Animal experiments again have supplied the rationale for its use to improve glycaemia, with results of such experiments suggesting that alpha lipoic acid can stimulate glucose transport into cells. The reason for the ability of alpha lipoic acid to benefit blood sugar control is not known. However the ability of other antioxidants to do likewise suggest that its capacity to reduce oxidative stress may play a pivotal role.
RdB