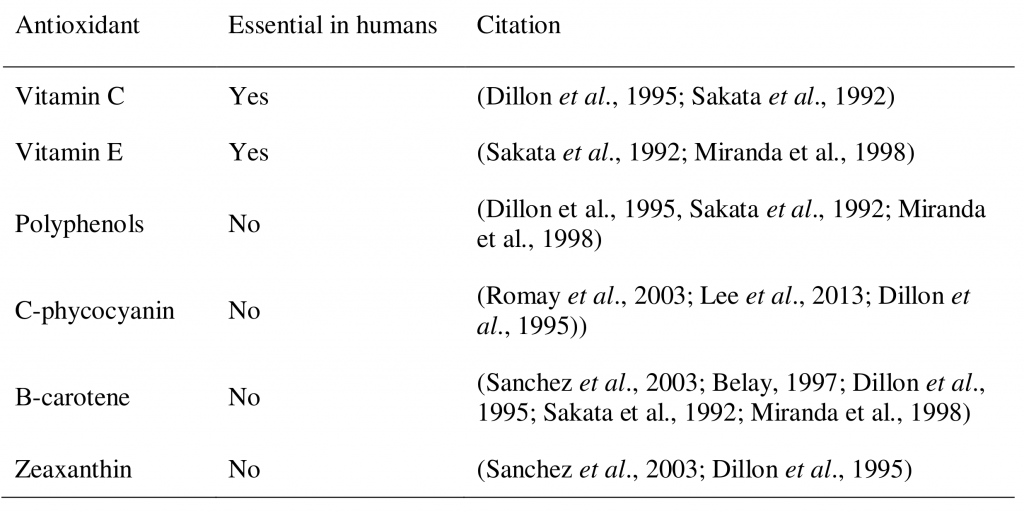
Spirulina maxima and Spirulina platensis belong to a group of filamentous photosynthetic cyanobacteria that can be found growing naturally in freshwater lakes of Asia, Africa and South America. Spirulina has traditionally been harvested, dried and used as a source of food for those people living around the lakes1. Spirulina platensis is commonly grown in tanks, freeze dried, and sold as a dietary supplement. Spirulina supplements have become popular in both tablet and powdered forms. Spirulina has been researched with respect to its health effect in humans and animals, and current evidence supports a role for spirulina extracts in the prevention of oxidative stress, inflammation and cancer2. Spirulina is a rich source of antioxidant nutrients and these may contribute to its health effects. Possible antioxidant nutrients in spirulina include vitamin C, vitamin E, polyphenols, carotenoids (β-carotene and zeaxanthin)and a photosynthetic accessory pigment called c-phycocyanin. These antioxidants are shown in table 1.
RdB